Scientists Discover Marine Fungus That Can Eat Plastic
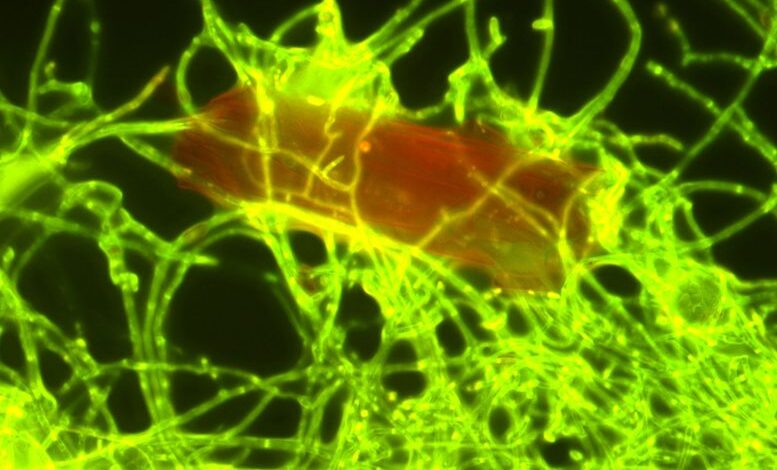
Researchers have found that the marine fungus Parengyodontium album can break down polyethylene in the ocean when exposed to UV light, suggesting the presence of more plastic-degrading fungi in deeper waters. A plastic particle (red) is colonized by the marine fungus Parengyodontium album. Credit: Annika Vaksmaa/NIOZ
Researchers found that the fungus Parengyodontium album degrades UV-exposed polyethylene in the ocean, suggesting that similar fungi might also break down plastics in deeper waters.
Researchers, including those from NIOZ, have discovered that a marine fungus can decompose the plastic polyethylene after it has been exposed to UV radiation from sunlight. Their findings, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, suggest that numerous other fungi capable of degrading plastic likely reside in the deeper regions of the ocean.
The fungus Parengyodontium album lives together with other marine microbes in thin layers on plastic litter in the ocean. Marine microbiologists from the Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (NIOZ) discovered that the fungus is capable of breaking down particles of the plastic polyethylene (PE), the most abundant of all plastics that have ended up in the ocean. The NIOZ researchers cooperated with colleagues from Utrecht University, the Ocean Cleanup Foundation and research institutes in Paris, Copenhagen, and St Gallen, Switzerland. The finding allows the fungus to join a very short list of plastic-degrading marine fungi: only four species have been found to date. A larger number of bacteria were already known to be able to degrade plastic.
Follow the degradation process accurately
The researchers went to find the plastic-degrading microbes in the hotspots of plastic pollution in the North Pacific Ocean. From the plastic litter collected, they isolated the marine fungus by growing it in the laboratory, on special plastics that contain labeled carbon. Vaksmaa: “These so-called 13C isotopes remain traceable in the food chain. It is like a tag that enables us to follow where the carbon goes. We can then trace it in the degradation products.”
Vaksmaa is thrilled about the new finding: “What makes this research scientifically outstanding, is that we can quantify the degradation process.” In the laboratory, Vaksmaa and her team observed that the breakdown of PE by P. album occurs at a rate of about 0.05 percent per day. “Our measurements also showed that the fungus doesn’t use much of the carbon coming from the PE when breaking it down. Most of the PE that P. album uses is converted into carbon dioxide, which the fungus excretes again.” Although CO2 is a greenhouse gas, this process is not something that might pose a new problem: the amount released by fungi is the same as the low amount humans release while breathing.
Only under the influence of UV
The presence of sunlight is essential for the fungus to use PE as an energy source, the researchers found. Vaksmaa: “In the lab, P. album only breaks down PE that has been exposed to UV-light at least for a short period of time. That means that in the ocean, the fungus can only degrade plastic that has been floating near the surface initially,” explains Vaksmaa. “It was already known that UV-light breaks down plastic by itself mechanically, but our results show that it also facilitates the biological plastic breakdown by marine fungi.”
Other fungi out there
As a large amount of different plastics sink into deeper layers before it is exposed to sunlight, P.album will not be able to break them all down. Vaksmaa expects that there are other, yet unknown, fungi out there that are degrading plastic as well, in deeper parts of the ocean. “Marine fungi can break down complex materials made of carbon. There are numerous amounts of marine fungi, so it is likely that in addition to the four species identified so far, other species also contribute to plastic degradation. There are still many questions about the dynamics of how plastic degradation takes place in deeper layers,” says Vaksmaa.
Plastic soup
Finding plastic-degrading organisms is urgent. Every year, humans produce more than 400 billion kilograms of plastic, and this is expected to have at least triple by the year 2060. Much of the plastic waste ends up in the sea: from the poles to the tropics, it floats around in surface waters, reaches greater depths at sea, and eventually falls down on the seafloor.
Lead author Annika Vaksmaa of NIOZ: “Large amounts of plastics end up in subtropical gyres, ring-shaped currents in oceans in which seawater is almost stationary. That means once the plastic has been carried there, it gets trapped there. Some 80 million kilograms of floating plastic have already accumulated in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre in the Pacific Ocean alone, which is only one of the six large gyres worldwide.”
Reference: “Biodegradation of polyethylene by the marine fungus Parengyodontium album” by A. Vaksmaa, H. Vielfaure, L. Polerecky, M.V.M. Kienhuis, M.T.J. van der Meer, T. Pflüger, M. Egger and H. Niemann, 26 April 2024, Science of The Total Environment.
DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.172819


