Researchers Identify Unique Early Biomarker


Researchers have identified miR-519a-3p as a potential early biomarker for Alzheimer’s, linked to prion protein expression, promising improvements in diagnosis and treatment for millions worldwide.
This molecule is directly associated with the expression of the cellular prion protein located on the surface of nerve cells. The research, conducted by the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia, paves the way for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease.
A new study conducted by the Molecular and Cellular Neurobiotechnology group at the Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC) and the University of Barcelona has discovered a novel biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease in its asymptomatic stages. The biomarker, miR-519a-3p, is a microRNA that is closely associated with the regulation of the cellular prion protein (PrPC). This protein is known to be deregulated in individuals afflicted with neurodegenerative conditions including Alzheimer’s disease.
The search for biomarkers that are stable and easily detectable in biofluids, such as microRNAs, offers hope for detecting Alzheimer’s disease in its early, asymptomatic stages. Early detection could significantly improve the diagnosis and treatment of this disease, which affects more than 35 million people worldwide.
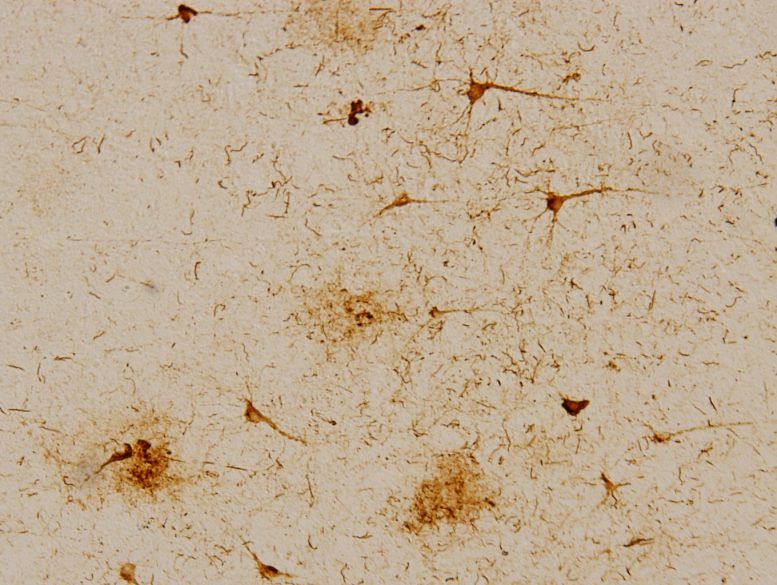
Light microscopy image of a section of post-mortem human frontal cortex from a patient with Braak grade VI (most advanced) Alzheimer’s disease. Neurons with high levels of tau protein can be seen. Credit: Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC)
First link between miR-519a-3p and PrPC in Alzheimer’s disease
The expression of some microRNAs is known to be deregulated in Alzheimer’s patients. However, this is the first time that this microRNA has been specifically linked to the decrease in cellular prion protein production during disease progression.
“Currently, tests to diagnose Alzheimer’s disease are usually carried out after the onset of symptoms, when there is already underlying cognitive impairment. We believe that the detection of this microRNA may help to establish additional criteria for a more accurate diagnosis in the early stages of the disease,” explains IBEC principal investigator José Antonio del Río, full professor at the Faculty of Biology and the Institute of Neurosciences of the University of Barcelona (UB) and co-leader of the study.

From left to right: Rosalina Gavín, José Antonio del Río and Dayaneth Jácome at IBEC laboratories. Credit: Institute for Bioengineering of Catalonia (IBEC)
The study also comparatively analyses the presence of the biomarker in samples from other neurodegenerative diseases: “If our goal is to use miR-519a-3p as a biomarker to detect Alzheimer’s dementia in hypothetically healthy people, it is essential to ensure that its levels are not altered in other neurodegenerative diseases. In our study, we compared the levels of this biomarker in samples from other tauopathies and Parkinson’s disease, confirming that the changes in miR-519a-3p are specific to Alzheimer’s disease,” said IBEC senior researcher Rosalina Gavín, UB associate professor and co-leader of the study.
Dayaneth Jácome, a researcher in del Río’s group and first author of the study, says that the team is making progress: The next step is to validate miR-519a-3p as a biomarker in blood samples from different cohorts of patients, in order to start using it in the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in peripheral samples.
The researchers are members of the Center for Networked Biomedical Research in Neurodegenerative Diseases, CIBERNED.
MicroRNAs: gene silencers
The amount of cellular prion protein changes over the course of Alzheimer’s disease, with higher levels in the early stages of the disease and lower levels as the disease progresses. Although the mechanism responsible for these changes is not known in detail, it has been observed that certain microRNAs bind to a specific region of the PRNP gene that controls PrPC expression, reducing it. For this reason, and based on comparisons of previous studies and computational analyses in various genomic databases, the researchers selected the microRNA miR-519a-3p for their study.
Reference: “miR-519a-3p, found to regulate cellular prion protein during Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis, as a biomarker of asymptomatic stages” by Dayaneth Jácome, Tiziana Cotrufo, Pol Andrés-Benito, Laia Lidón, Eulàlia Martí, Isidre Ferrer, José Antonio del Río and Rosalina Gavín, 21 April 2024, Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease.
DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2024.167187


